Have you ever woken up with itchy bites and wondered what caused them? Bed bugs are notorious for their stealthy nature and can turn a peaceful night into a restless one. Understanding their impact is crucial.
Many people associate bed bugs solely with discomfort, but there’s a lingering question: bed bug causes what disease? While these pests are primarily a nuisance, their presence can lead to more serious health concerns.
In this article, we’ll explore the myths surrounding bed bugs and their potential health risks. You might be surprised to learn about the various factors that contribute to the fear surrounding these tiny insects.
Join us as we uncover the truth behind the diseases spread by bed bugs, separating fact from fiction while exploring the real implications of an bed bug infestation.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Bed Bugs
Biology of Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are small, wingless insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. Their size allows them to hide easily in various places, making them difficult to detect. Understanding their anatomy is essential for effective management.
Life Cycle of Bed Bugs
The life cycle of a bed bug consists of several stages, including:
- Eggs: Tiny, white eggs that can hatch in about a week.
- Nymphs: Young bed bugs that molt several times before reaching adulthood.
- Adults: Fully grown bed bugs that can survive for months without feeding.
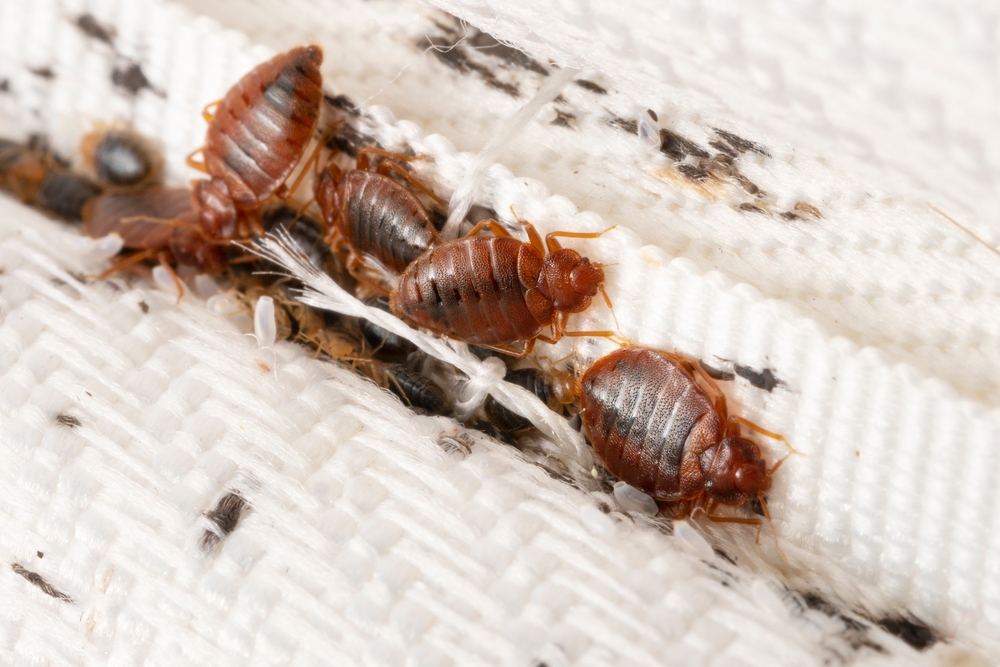

Habitat Preferences and Behavior
Bed bugs thrive in environments where they can easily access hosts. They prefer areas that are warm and dark, often hiding in:
- Mattresses: The most common hiding spots.
- Bed frames: Cracks and crevices provide ideal shelter.
- Couches and chairs: Upholstered furniture is also a favorite.
Signs of Infestation
Identifying a bed bug infestation early can prevent further problems. Common signs include:
- Bites: Itchy welts on the skin, usually in a line or cluster.
- Fecal spots: Dark stains on bedding or furniture.
- Shed skins: Nymphs shed their exoskeletons as they grow.
If you suspect an infestation, taking immediate action is crucial to control the spread and minimize health risks associated with these pests.
Health Risks Associated with Bed Bugs
Direct Effects of Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites can cause a range of reactions in individuals. While some may experience no symptoms, others can suffer from significant discomfort. Understanding the effects of bed bug bites is essential for addressing potential health issues.
Common Allergic Reactions and Symptoms
The most common reactions to bed bug bites include:
- Red welts: Raised, itchy bumps that appear on the skin.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the bite area, which may vary in size.
- Blistering: In severe cases, blisters can develop from scratching.
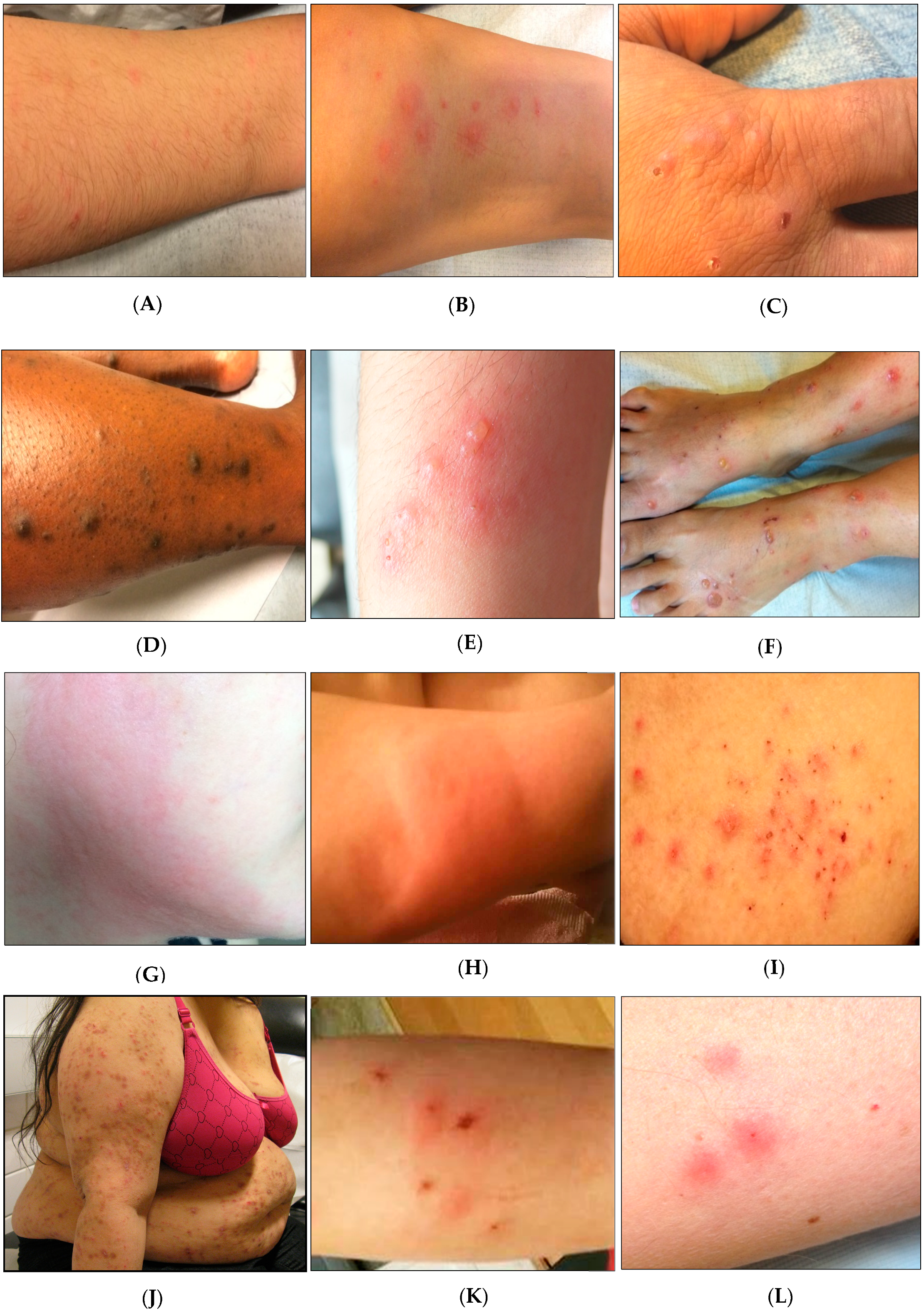
Potential for Secondary Infections
Scratching bed bug bites can lead to secondary infections. When the skin barrier is broken, bacteria can enter and cause complications. It is important to manage itching and avoid scratching to minimize this risk.
Psycho-social Impact of Infestations
The presence of bed bugs can have a significant psychological impact on affected individuals. The stress and anxiety associated with an infestation can lead to:
- Sleep deprivation: Difficulty sleeping due to fear of bites or discomfort.
- Anxiety: Constant worry about the infestation spreading or recurring.
- Social stigma: Feelings of embarrassment or shame that may affect social interactions.
Recognizing these health risks is crucial for individuals dealing with bed bug infestations, as both physical and mental well-being can be affected.
Also Read: What Causes Bed Bugs? 7 Factors That Attract Them to Your Home
Bed Bugs Disease Transmission Myths
Current Scientific Consensus
There is a common belief that bed bugs can transmit diseases. However, current research indicates that bed bugs are not considered effective vectors for major diseases. Understanding this scientific consensus can help alleviate unnecessary fears.
Why Bed Bugs Are Not Vectors
Several factors contribute to the conclusion that bed bugs do not spread diseases:
- Feeding habits: Bed bugs feed on blood but do not inject saliva into the bloodstream in a way that transmits pathogens.
- Life cycle: Their life cycle does not support the development of pathogens that could be transmitted to humans.
- Limited host range: Bed bugs primarily feed on humans and a few other mammals, reducing their potential to spread diseases.
Potential Pathogens Found in Bed Bugs
While bed bugs may carry certain microorganisms, the evidence of disease transmission is lacking. Some of the pathogens associated with bed bugs include:
- Coxiella burnetii: A bacterium linked to Q fever, though transmission through bed bugs is unproven.
- Trypanosoma cruzi: The causative agent of Chagas disease, but again, no confirmed cases of transmission via bed bugs.
The Importance of Awareness
Understanding these myths and the actual risks associated with bed bugs can help individuals respond more effectively to infestations. Awareness allows for better management strategies without inciting undue panic regarding disease transmission.
Case Studies Highlighting Bed Bug Infestations
Case Study 1: Urban Apartment Complex
An urban apartment complex faced a significant bed bug infestation that affected multiple units. Residents reported itchy bites and discomfort, leading to widespread concern among tenants. The management had to act quickly to address the issue.
Management Response
The property management implemented a comprehensive pest control strategy, which included:
- Inspection: Thorough inspections of all affected units to assess the extent of the infestation.
- Treatment: Professional extermination services were hired to eliminate bed bugs using heat treatment and chemical solutions.
- Follow-up: Regular follow-ups were conducted to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Health Consequences Experienced by Residents
The aftermath of the infestation revealed various health impacts on residents. Many experienced increased anxiety and sleep disturbances due to the fear of bites. Some individuals also developed secondary infections from scratching their bites.
Case Study 2: Nursing Home Infestation
A nursing home experienced a bed bug infestation that posed serious risks to its vulnerable residents. Given the elderly population, the management had to be particularly cautious in addressing the situation.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
The presence of bed bugs in such facilities can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Increased stress: Residents faced heightened anxiety about their living conditions and potential bites.
- Health complications: Some residents developed skin infections due to scratching, which required medical attention.
- Social isolation: Fear of infestations led some residents to withdraw from social interactions.
Measures Taken to Control the Infestation
The nursing home implemented strict measures to control the bed bug problem, including:
- Staff training: Educating staff on identifying signs of bed bugs and proper reporting procedures.
- Regular inspections: Conducting routine inspections in resident rooms and common areas.
- Pest control partnerships: Collaborating with pest control experts for effective treatment plans.
These case studies illustrate the real-world implications of bed bug infestations and highlight the importance of prompt action in mitigating health risks associated with these pests.
Prevention and Control Strategies
Effective Pest Management Techniques
Controlling bed bugs requires a combination of effective pest management techniques. Understanding these methods can help prevent infestations and manage existing ones. Here are some key strategies:
Professional Extermination Methods
Hiring professionals is often the most effective way to eliminate bed bugs. Common methods include:
- Heat treatment: Raising the temperature in infested areas to kill bed bugs at all life stages.
- Chemical treatments: Applying insecticides specifically designed for bed bugs, ensuring safety for residents.
- Integrated pest management: Combining various strategies for long-term control and prevention.
Best Practices for Homeowners
Homeowners can take proactive steps to prevent bed bug infestations. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Regular inspections: Routinely check bedding, furniture, and luggage for signs of bed bugs.
- Protective covers: Use mattress and box spring encasements to prevent bed bug access.
- Decluttering: Reduce clutter in living spaces to minimize hiding spots for bed bugs.
Travel Precautions
Traveling can expose individuals to bed bugs. Taking precautions while away from home is essential:
- Luggage care: Keep luggage off the floor and use hard-sided cases when possible.
- Hotel checks: Inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs upon arrival.
- Laundry precautions: Wash and dry clothes on high heat immediately after returning home.
By implementing these prevention and control strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of encountering bed bugs and their associated health risks.

Frequently Asked Questions - FAQS
Q. Can bed bug bites cause serious skin infections like cellulitis or impetigo?
A. Yes, bed bug bites can lead to serious skin infections such as cellulitis or impetigo if the skin is broken from scratching. It is important to keep bite areas clean and avoid excessive scratching to reduce infection risk.
Q. What are the long-term health effects of repeated bed bug bites and infestations?
A. Repeated bed bug bites can lead to chronic skin issues, psychological stress, and conditions like anxiety or insomnia. Long-term exposure may also exacerbate existing health conditions and affect overall well-being.
Q. Is it possible to develop an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis to bed bug saliva?
A. Yes, some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to bed bug saliva, which can range from mild itching to severe reactions like anaphylaxis. Severe symptoms require immediate medical attention for proper management.
Q. Can bed bugs transmit diseases like MRSA, hepatitis, or HIV through their bites?
A. Bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases such as MRSA, hepatitis, or HIV. While they can carry pathogens, there is currently no evidence that they effectively spread these diseases through bites.
Q. How do I know if my bed bug bites are infected and require medical treatment?
A. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or fever at the bite site. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical treatment to prevent further complications.
Q. What are the symptoms of a severe bed bug bite allergy, and when should I see a doctor?
A. Severe allergic reactions may include intense itching, swelling, hives, or difficulty breathing. If these symptoms occur after a bed bug bite, it is essential to see a doctor immediately for evaluation and treatment.
Q. Can bed bug bites cause psychological issues like anxiety, insomnia, or PTSD?
A. Yes, living with a bed bug infestation can lead to significant psychological issues such as anxiety, insomnia, and even PTSD. The stress of dealing with infestations can have lasting effects on mental health.
Q. Are there any specific diseases that make people more susceptible to bed bug infestations or reactions?
A. Individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic skin conditions may be more susceptible to bed bug infestations and reactions. Conditions like eczema can worsen due to scratching and irritation from bites.
Q. Can bed bug bites worsen existing skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis?
A. Yes, bed bug bites can exacerbate existing skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. The irritation from bites may trigger flare-ups, leading to increased discomfort and inflammation in affected areas.
Q. What are the best ways to treat infected bed bug bites at home and when to seek professional help?
A. To treat infected bed bug bites at home, clean the area with soap and water, apply antiseptic ointment, and use antihistamines for itching. Seek professional help if symptoms worsen or do not improve within a few days.
Q. How can I distinguish between bed bug bite reactions and other skin diseases like scabies or hives?
A. Bed bug bite reactions typically appear as red, itchy bumps in clusters or lines on exposed skin. In contrast, scabies often presents with intense itching and rash in webbed areas of the body while hives appear as raised welts.
Q. Do bed bug bites pose a greater health risk to children, the elderly, or people with weakened immune systems?
A. Yes, children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems face greater health risks from bed bug bites due to their potentially severe reactions and increased vulnerability to infections from scratching.
Q. Can scratching bed bug bites lead to secondary infections and scarring?
A. Yes, scratching bed bug bites can break the skin barrier, leading to secondary infections and potential scarring. It is advisable to avoid scratching and keep the area clean to minimize these risks.
Q. Are there any studies linking bed bug infestations to the spread of specific infectious diseases?
A. Current research does not support a strong link between bed bug infestations and the spread of specific infectious diseases. While they may harbor pathogens, effective transmission through bites has not been established.
Q. What are the mental health implications of living with a persistent bed bug infestation?
A. Living with a persistent bed bug infestation can lead to significant mental health issues such as chronic stress, anxiety disorders, and social isolation due to embarrassment about potential infestations being discovered by others.
Q. Can bed bug bites cause swollen lymph nodes or other systemic symptoms?
A. In some cases, severe allergic reactions to bed bug bites may result in swollen lymph nodes along with systemic symptoms such as fever or malaise. These symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation for appropriate care.
Q. How can I prevent bed bug bites from becoming infected after being bitten?
A. To prevent infection after being bitten by a bed bug, wash the area gently with soap and water immediately after noticing a bite, apply an antiseptic cream if needed, and avoid scratching the affected area.
Q. What are the differences in allergic reactions to bed bug bites between different individuals?
A. Allergic reactions to bed bug bites vary widely among individuals; some may experience mild itching while others suffer severe swelling or systemic reactions like difficulty breathing depending on their immune response.
Q. Is there any research on the impact of bed bug bites on respiratory health, such as asthma?
A. Research indicates that while direct links between bed bug bites and respiratory issues like asthma are limited, anxiety from infestations could exacerbate existing respiratory conditions due to stress-related triggers.
Q. Beyond skin irritation, what are the potential long-term health consequences of chronic bed bug exposure?
A. Chronic exposure to bed bugs may lead not only to persistent skin irritation but also significant psychological impacts such as anxiety disorders and sleep disturbances that can affect overall quality of life over time.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Throughout this article, we explored the various aspects of bed bugs and their potential health implications. Understanding the truth behind bed bug causes what disease helps dispel common myths and reduce unnecessary fears.
Health Risks and Misconceptions
While bed bug bites can lead to discomfort and psychological stress, the evidence does not support the idea that they are significant vectors for disease. Awareness of these facts is crucial for effective management.
The Importance of Proactive Measures
Preventing bed bug infestations requires vigilance and proactive strategies. By implementing effective pest management techniques and maintaining awareness, individuals can protect themselves from the potential health risks associated with these pests.
Final Thoughts
Bed bugs may be a nuisance, but understanding their behavior and health implications empowers individuals to take action. Staying informed and prepared is key to minimizing their impact on our lives.

